Words to know for chapter 1:
Overwhelmed - feeling like you have so much to do that you can't even get started
Disorder - something that doesn't work quite right
Processing - how your brain uses information
Discrepancy - a difference between two things
Ability - what you are able to do
Achievement - what you have already done
Storage - putting something away for safe keeping
Retrieval - getting something out of storage
Basic Reading - sounding out words
Reading Comprehension - understanding what you have read
Math Calculation - solving basic number problems
Math Reasoning - solving story problems or real-life math situations
Written Expression - giving information in writing
Oral Expression - giving information by talking
Listening Comprehension - understanding what you hear
Compensate - using a strength to make up for a weakness
Interfere - get in the way

The case begins
'A good detective starts each case by asking questions to find out about the mystery to be solved. But first, we need to find out what clues you already know.'
You already know that a learning disability makes you feel overwhelmed by schoolwork.............
You just can't seem to get assignments done on time...............
And it is hard (maybe even scary) to begin big projects..............
But worst of all..........sometimes a learning disability just makes you feel dumb.
'So why is school so difficult for you? That is the real mystery!!'

'Before we can really begin solving the mysteries of your learning disability, we need to ask a few important questions:'
What is a Learning disability?
Definition: A 'learning disability' is a disorder in one or more of the basic psychological processes involved in understanding and using language spoken or written which may manifest itself in an imperfect ability to listen, think, speak, read, spell, or do mathematical calculations.
Wow, is that ever confusing?!!! What does it mean?
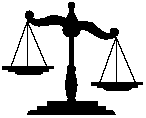
Well, that's the legal definition. There are really 2 parts to a learning disability.
and
Discrepancy
First, having a learning disability means that your brain 'processes' information differently than most other students. Certain kinds of information get stuck or lost while traveling through your brain.
Second, having a learning disability causes a 'discrepancy' between your ability and your achievement. This means that you are a lot smarter than you perform in school. You might be just as smart as someone sitting next to you in class, but your grades in certain areas aren't as good. This isn't because you are dumb, lazy, or anything else bad. You just learn differently.
It's kind of like a baseball player who has the 'ability' to hit home runs but is given a broken bat to use. He doesn't have the chance to prove how great he really is.

An LD student often has trouble proving how smart he or she is.
Explain more about information processing.
Information processing refers to how your brain:
Takes in information,
Uses this information,
Stores the information in memory,
Retrieves the information from memory, and
Expresses the information
Students with learning disabilities struggle with certain
kinds of learning because their brains have difficulty 'processing' certain kinds of information. It is like when you go on a car trip and get stuck in road construction. It takes you a lot longer to get where you are going. Its the same with information going through your brain.
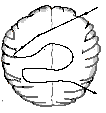
Information gets 'bogged down' in certain areas of an LD brain. When information gets bogged down, it is much more difficult to learn.
Different kinds of information travel through different parts of the brain. That's why some information is learned quickly and easily while other information is much more difficult.

What learning areas are affected?
A learning disability can affect:
Basic Reading
Reading Comprehension
Math Calculation
Math Reasoning
Written Expression
Oral Expression
Listening Comprehension
Why do I get 'Special Education' help?
Each State has rules about who can receive special education services. Because these services are very expensive you have to 'qualify' according to the rules of the State.
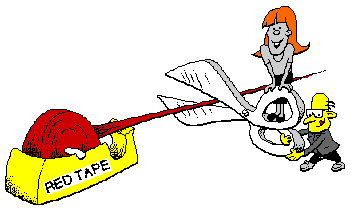
For LD services you have to prove that your learning difficulty is caused by the way your brain processes information. You also have to prove that your processing difficulty causes a 'severe discrepancy' between what you should be able to learn (how smart you are) and how much you have learned (your achievement). You are given special tests to find out if you qualify for special education services because of a learning disability.
Are all LD students alike?
No. But many LD students experience very similar processing and learning difficulties. And all LD students get frustrated in school.

Will I ever get over my learning disability?
A true learning disability never goes away. But, with understanding and effort you can learn to use your many strengths to 'compensate' for your weaker processing skills. You may also be able to strengthen your weak processing skills so that your learning disability is not as severe. Many LD people are highly creative and 'gifted' in many ways. Even many famous and very successful people have learning disabilities.
Is a learning disability the same as Dyslexia?
Dyslexia is simply a fancy word for a learning disorder that involves reading. Other similar terms include Dysgraphia (writing disorder) and Dyscalcula (math disorder). We will learn more about those and other LD terms later.
'Good detective work!! Your questions have
uncovered several  very important clues:'
very important clues:'
1. A learning disability involves how your brain processes information, not how smart you are.
2. A learning disability causes a 'discrepancy' between your ability and your achievement, so you can't always show how smart you are in school.
3. A learning disability lasts your whole life.
'The case is off to a great start!!'
And here is something you might find interesting. Many famous and highly successful people have learning disabilities including:
'These people didn't let their learning disabilities get in the way of their dreams. You shouldn't either!'
Review questions:
1. What are the two main parts of a learning disability?
2. What does 'processing' mean?
3. What does 'discrepancy between ability and achievement' mean?
4. True or false: A 'processing disability' is like a fast car that is 'stuck' in traffic.
5. True or false: All LD students are alike.
6. True or false: Most LD students get frustrated by their learning problems.
7. Does a true learning disability ever go away completely?
8. Can your learning disability improve?
9. True or false: You can't really be successful if you have a learning disability.
Want to find out more about learning disabilities?
• Explore the library for information about learning disabilities or special education.
• Do an internet search for 'learning disabilities'.
• Talk to your LD teacher or school psychologist.
Return to the LDinfo Web Site to find out about any of the following topics (and more):
Learning disabilities - what is a learning disability (LD or SLD)?
Dyslexia: Dyslexia is a reading disability or reading disorder
Dysgraphia Dysgraphia is a writing disability or disorder
Dyscalculia Dyscalculia is a math disability or disorder
What is an attention deficit disorder (ADD, AD/HD, ADHD)?
Gifted LD: Can a student be gifted and LD?
Emotional/Behavioral issues and LD: Do LD students experience behavior problems or depression?
Section 504: What is a Section 504 plan?
What is special education?
What is processing?
What is a severe discrepancy?
What is a nonverbal learning disability (nonverbal LD or NLD)?
What is a central auditory processing disorder (CAPD)?
Uncovering the Mysteries of your Learning Disability
Order printed copies of this manual
- Chapter 1 - What is a Learning Disability?
- Chapter 2 - What Causes Learning Disabilities?
- Chapter 3 - Discrepancy = Underachievement
- Chapter 4 - Processing: The Sensory Channels
- Chapter 5 - Processing: The Cognitive Channels
- Chapter 6 - Processing: Sensory + Cognitive
- Chapter 7 - LD Jargon
- Chapter 8 - Using Accommodations
- Chapter 9 - Other Issues Related to LD
- Chapter 10 - Intelligence vs IQ
- Chapter 11 - Exercizing Your Weakness
- Chapter 12 - LD and the Law
- Chapter 13 - Becomming an Effective Self-Advocate
- Chapter 14 - Planning for Your Future
- Chapter 15 - The Summary
Copyright © 2006-2017 LDinfo Publishing
All rights reserved. Any reuse or republishing of the text
or images on this web site without prior written consent of
the copyright holder is prohibited.